If you’re leading a business, team, or department, you’ve likely faced the challenge of turning strategy into action. That’s where the Balanced Scorecard (BSC) comes in. It’s a simple but powerful framework that helps organizations measure what matters most—and stay focused on strategic goals.
In this article, we’ll break down what the Balanced Scorecard is, why it’s useful, and how to use it effectively—even if you’re not a strategy expert.
What Is the Balanced Scorecard?
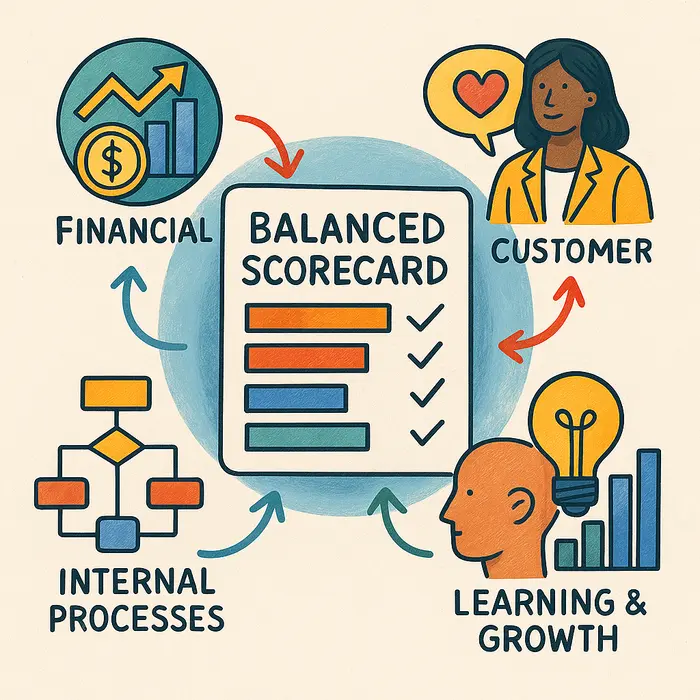
The Balanced Scorecard is a performance management tool developed by Robert Kaplan and David Norton. It helps organizations track performance from multiple angles—not just financials.
The four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard:
- Financial – Are we delivering value to shareholders or owners?
- Customer – Are we meeting customer needs and expectations?
- Internal Processes – Are our operations efficient and effective?
- Learning and Growth – Are we improving and preparing for the future?
Together, these perspectives provide a more complete view of performance than financials alone.
Why Use the Balanced Scorecard?
The BSC helps organizations:
- Align daily work with long-term strategy
- Measure performance beyond just profits
- Spot gaps and imbalances in business health
- Create focus and accountability at all levels
It’s especially useful in environments where strategy execution is a struggle or where teams operate in silos.
Example: Balanced Scorecard in Action
Let’s say you run a regional logistics company. Your Balanced Scorecard might include:
- Financial: Increase profit margin by 5%
- Customer: Improve customer satisfaction to 90%
- Internal Processes: Reduce delivery delays by 20%
- Learning and Growth: Provide monthly training to all drivers
Each of these goals would have associated KPIs and initiatives.
How to Build a Balanced Scorecard
Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
1. Clarify Your Strategy
Start by identifying your strategic goals. What are you trying to achieve over the next 1–3 years?
2. Define Objectives for Each Perspective
Translate your strategy into specific goals for each of the four BSC perspectives.
3. Choose Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Pick 1–3 measurable indicators per objective. Keep it simple and relevant.
4. Set Targets and Initiatives
For each KPI, define a target value and a project or action to help you reach it.
5. Monitor and Review
Regularly review the scorecard to track progress, adjust actions, and learn what’s working.
Tips for Using the Balanced Scorecard Well
- Keep it focused. Don’t overload each perspective—aim for clarity, not complexity.
- Link it to real work. Make sure daily activities connect to scorecard goals.
- Communicate it clearly. Share it across the organization so everyone knows the priorities.
- Use it as a learning tool. The scorecard isn’t just about tracking—it’s about improving.
Balanced Scorecard vs. Other Tools
| Tool | Focus | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| KPI Dashboard | Tracks metrics | Operational monitoring |
| OKRs | Sets goals and outcomes | Agile goal setting |
| Balanced Scorecard | Aligns strategy and performance | Strategy execution and alignment |
These tools can complement each other—many organizations use all three.
Summary: A Tool to Bring Strategy to Life
The Balanced Scorecard helps leaders move beyond vague goals and gut feelings. It turns strategic intent into measurable action across four key areas: finance, customers, operations, and growth.
Key Takeaways:
- The BSC offers a balanced view of performance, not just financials
- It aligns work with strategy and drives accountability
- You can start simple, refine over time, and use it to lead with clarity